Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are essential proteins of the immune system that can specifically recognize and bind to foreign molecules (antigens) such as proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. Their unique ability to detect target molecules with high specificity makes them indispensable tools in molecular biology, immunology, and diagnostics.
Definition of Antibodies
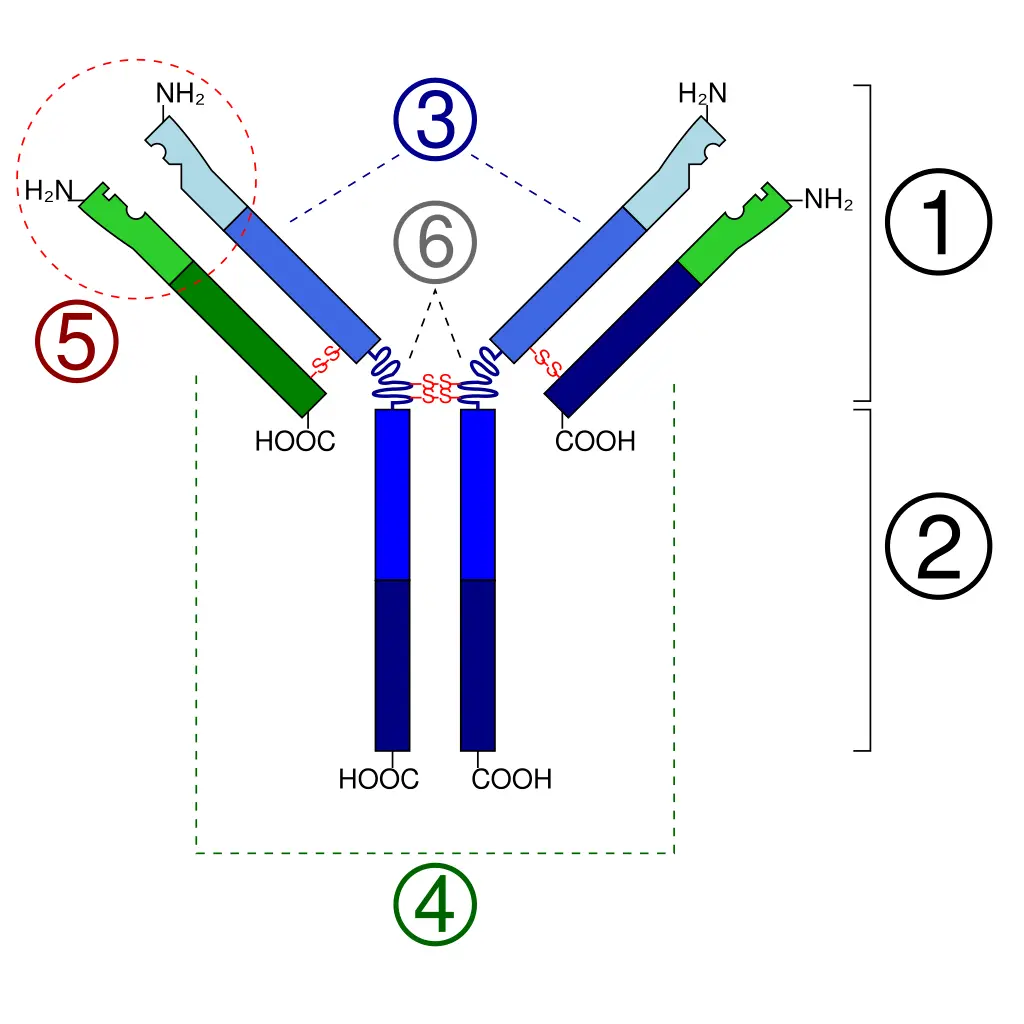
An antibody is a glycoprotein produced by plasma cells (derived from B lymphocytes) in response to an antigen. Its characteristic Y-shaped structure is composed of:
- two heavy chains,
- two light chains,
- variable regions (Fab) that recognize and bind to the specific antigen,
- a constant region (Fc) that mediates immune responses.
Monoclonal Antibodies: Types and Applications
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are produced by a single clone of hybrid B cells (hybridomas) and bind to one specific epitope on an antigen.
🔬 Applications: diagnostics, targeted therapies, research (e.g., precise detection of a protein target in tissues).
Polyclonal antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies are a mixture of different antibodies produced by various B cells that recognize multiple epitopes on the same antigen.
🔬 Applications: western blotting, immunoprecipitation, ELISA — ideal when a strong signal is needed.
Primary and secondary antibodies
- Primary antibodies: bind directly to the antigen.
- Secondary antibodies: bind to primary antibodies and are often conjugated to markers (enzymes, fluorophores) for detection and signal amplification.
Recombinant antibodies
Produced using expression systems (bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells), recombinant antibodies are designed for high specificity and batch-to-batch consistency.
🔬 Advantage: low variability between lots.
Conjugated antibodies
These are antibodies linked to detectable agents:
- Fluorophores (for immunofluorescence, flow cytometry)
- Enzymes (HRP, alkaline phosphatase) for ELISA, western blot
- Radioisotopes for imaging applications
Key Techniques Using Antibodies
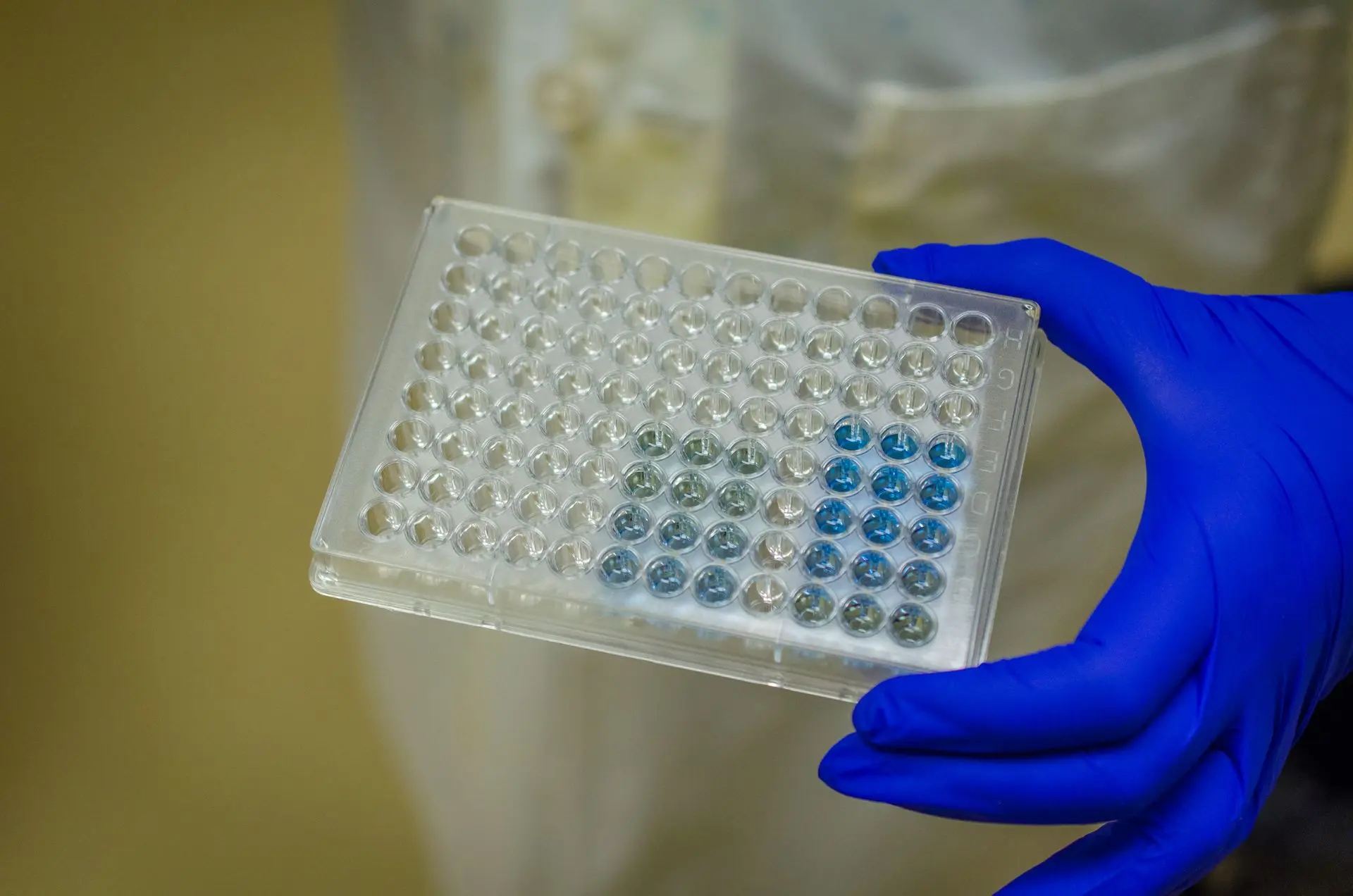

ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
Quantitative method to measure antigen or antibody levels in a sample, based on an enzyme reaction that produces a color change .
Western blotting
Technique to detect proteins separated by electrophoresis, transferred onto a membrane, and probed with specific antibodies.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Used to localize antigens in tissue sections. Antibodies are visualized using enzyme or fluorescent labels.